Projects
Our department is involved in several projects with international partners. Our contribution to the different consortia consits of electronics development, detectors characterisation and software design. Along with these projects we developed our near-infrared speckle camera system which operates at several telescopes.
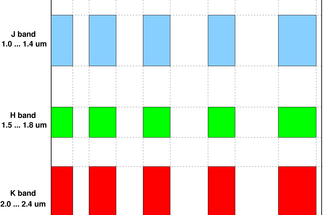
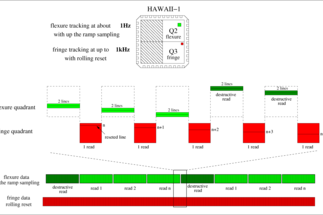
AMBER (Astronomical Multi BEam Recombiner) is one of the first-generation ESO VLTI (Very Large Telescope Interferometer) instruments. It provides interferometric beam combination in the near-infrared domain from 1 to 2.4 μm (J, H and K bands).
[more]
ARGOS (Advanced Rayleigh guided Ground layer adaptive Optics System) is the Laser Guide Star and wavefront sensing facility for the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT).
[more]
LINC-NIRVANA (
LBT
INterferometric
Camera -
Near-
IR /
Visible
Adaptive I
Nterferometer for
Astronomy) is built for one of the most exciting new astronomical telescopes, the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) on Mt. Graham in Arizona, USA. With its two 8.4 m primary mirrors, the design makes possible near-infrared (1 - 2.4 µm) interferometric observations with a maximum baseline of 23 m.
[more]
MATISSE (Multi-Aperture mid-Infrared SpectroScopicExperiment) is a second-generation interferometry instrument for the ESO Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI). The interconnection of three or four telescopes makes it possible to capture visibilities and closure phases and allows pictures in the mid infrared range to be reconstructed. The maximum baseline length of 200 m (the distance between two telescopes) makes for a high resolution in the generated images.
[more]
Speckle interferometry allows the reconstruction of high resolution diffraction-limited images. Due to atmospheric turbulences, the image resolution (seeing) degrades even for large telescopes to about 1 arcsec at visible wavelengths. However, the theoretical diffraction-limited angular resolution is given by lamda/D. For example the diffraction limit for observations at 600 nm wavelength at a telescope of 6 m diameter is 0.02 arcsec, a factor of 50 better than the seeing limit.
[more]